A beginner's guide to 7 types of SQL JOINs
After working with SQL for a while, you just realized that JOIN is one of the most important SQL queries and it’s frequently used across any relational databases. This post is going to introduce 7 types of SQL JOINs and how to use them in practices.
Different database management systems have different functions and extensions, thus the syntax might vary, but they all use standard SQL and if you learn these SQL JOINs concepts below, you will be able to pick up syntax easily for each database.
What is a JOIN in SQL?
JOIN is a clause used in SQL to link data from one table to another table using one or more data column shared between two tables.
In other words, we combine data of the two existing tables into one. For example, table1 has data about x and y, table2 has data about y and z, so we join table1 and table2 to get a table3 with all data of x, y, and z.
How important is JOIN in SQL?
For storing data, it’s not efficient to put everything into one table as it makes the table become heavier and lower its performance a lot. So it’s better to divide information into many different tables, faster storing, faster retrieving. But every now and then, you will need to select data from multiple tables, that’s where JOIN comes in handy.
Normally a JOIN has an ON condition and depending on the type of JOINs, it will return all the record from one table, or both, if there’s a match with the ON condition.
7 types of JOINs and how to use them
Here is the list of 7 types of JOINs that you are going the use quite a lot in SQL.
- INNER JOIN
- FULL [OUTER] JOIN
- FULL [OUTER] JOIN without the intersection
- LEFT [OUTER] JOIN
- LEFT [OUTER] JOIN without the intersection
- RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN
- RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN without the intersection
Let’s dive in.
1. INNER JOIN
INNER JOIN returns all records that are commonly shared between two tables, or those records that exist in both tables that match the ON condition. From the picture below, we can see that it’s the intersection between two tables.
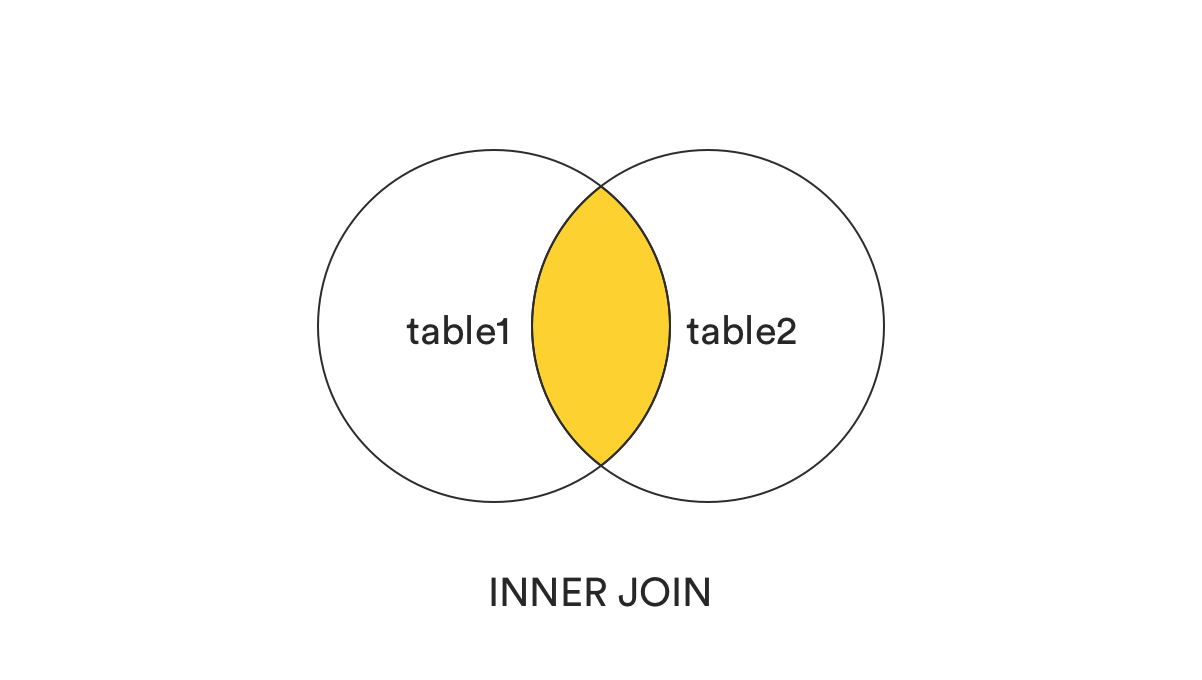
This is perhaps the most frequently used SQL JOIN clause.
SQL syntax:
SELECT *
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2;
2. FULL [OUTER] JOIN
FULL [OUT] JOIN returns all the records that match the ON condition, no matter which table they are stored in. It can be from table1, table2, or both.
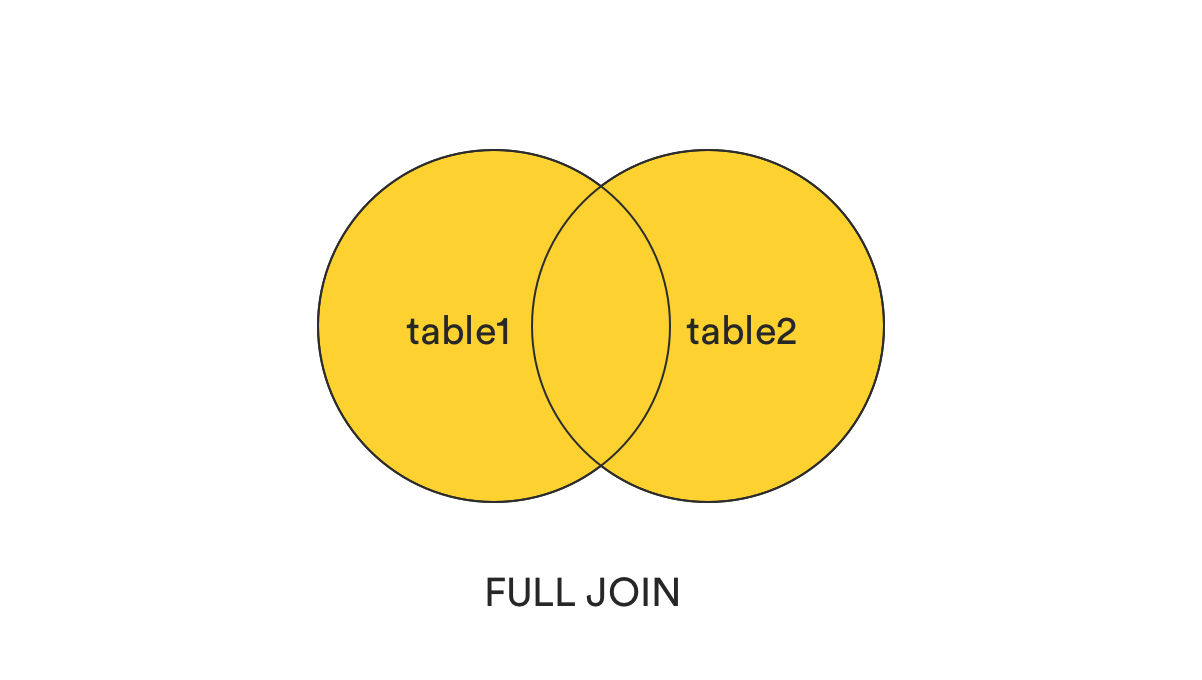
SQL syntax:
SELECT *
FROM table1
FULL JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2;
3. FULL [OUTER] JOIN without the intersection.
This clause returns all records that match the ON condition, excluding those are in common between two tables, or those records exist in both tables.
In plain term, it can be understood as (OUTER JOIN) - (INNER JOIN).
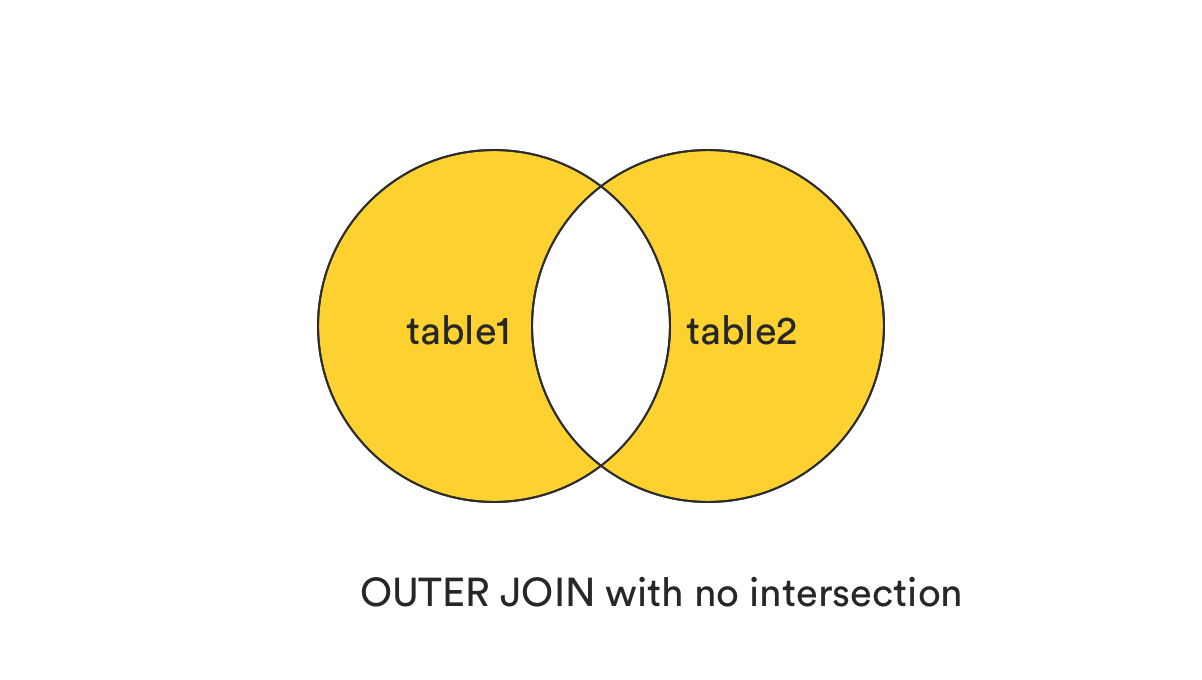
SQL syntax:
SELECT *
FROM table1
FULL JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2
WHERE table1.col1 IS NULL
OR table2.col2 IS NULL;
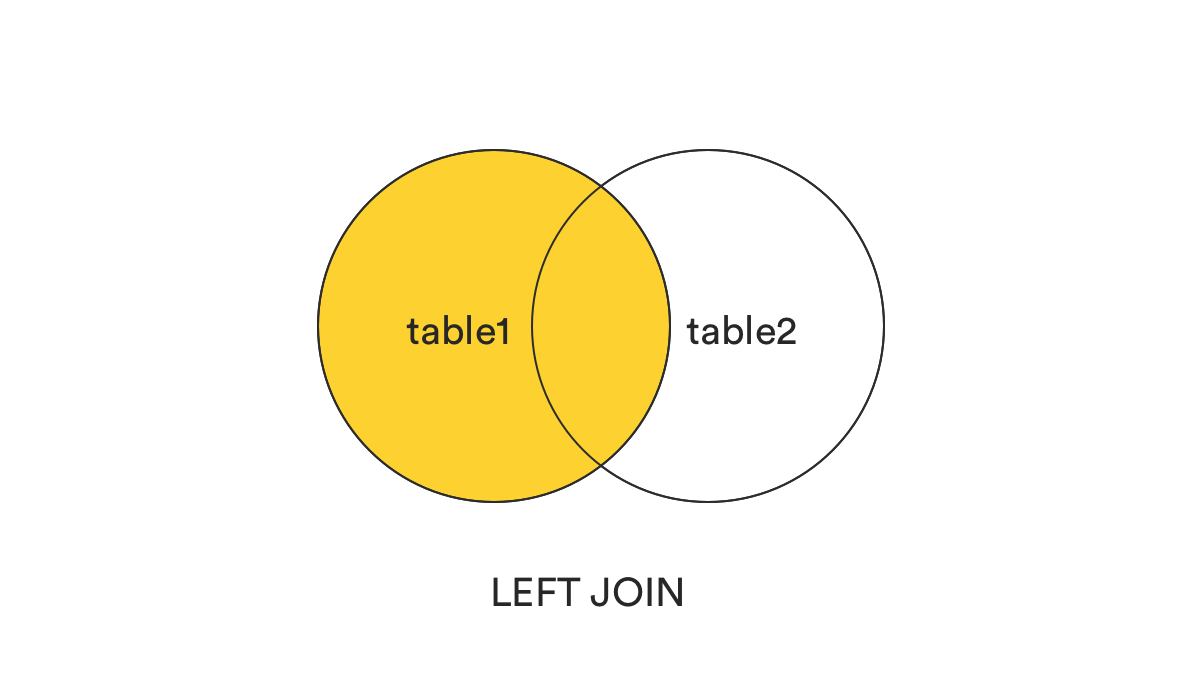
4. LEFT [OUTER] JOIN
LEFT JOIN returns all records from the left table (table1) that matched the ON condition.
SQL syntax:
SELECT *
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2;
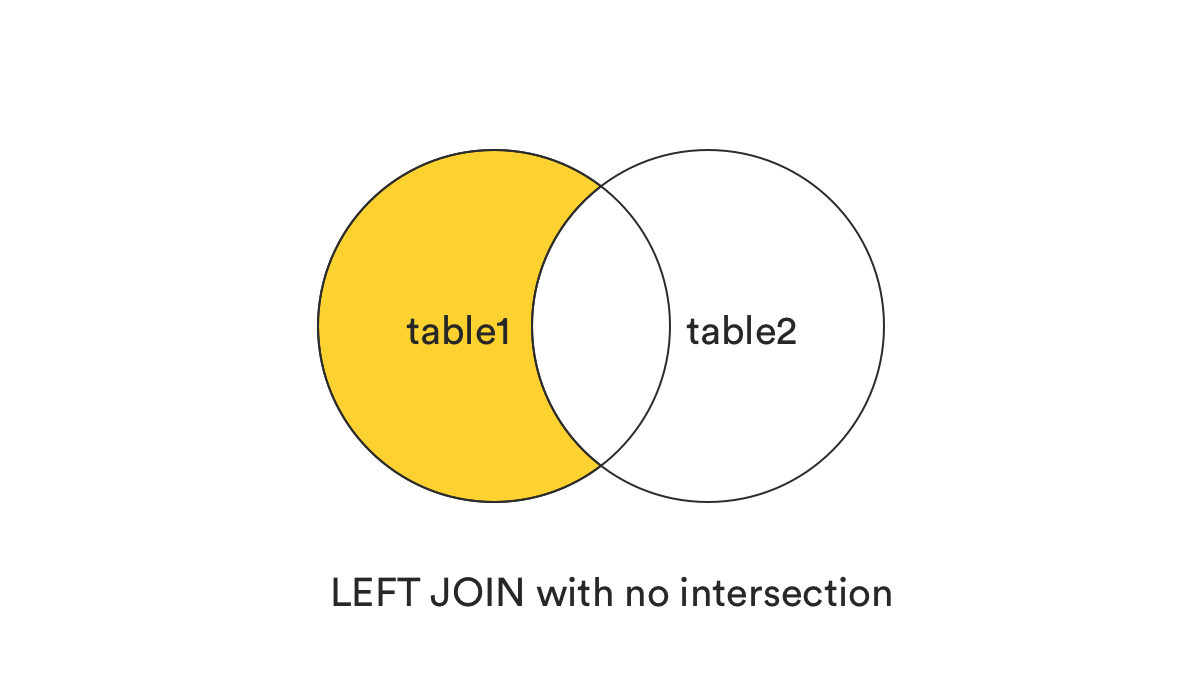
5. LEFT [OUTER] JOIN without the intersection
This clause returns all records from the left table (table1) that matched the ON condition, but exclude those are in common better two tables, or those records exist in both tables.
In plain term, it can be understood as (LEFT JOIN) - (INNER JOIN).
SQL syntax:
SELECT *
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2
WHERE table2.col2 IS NULL;
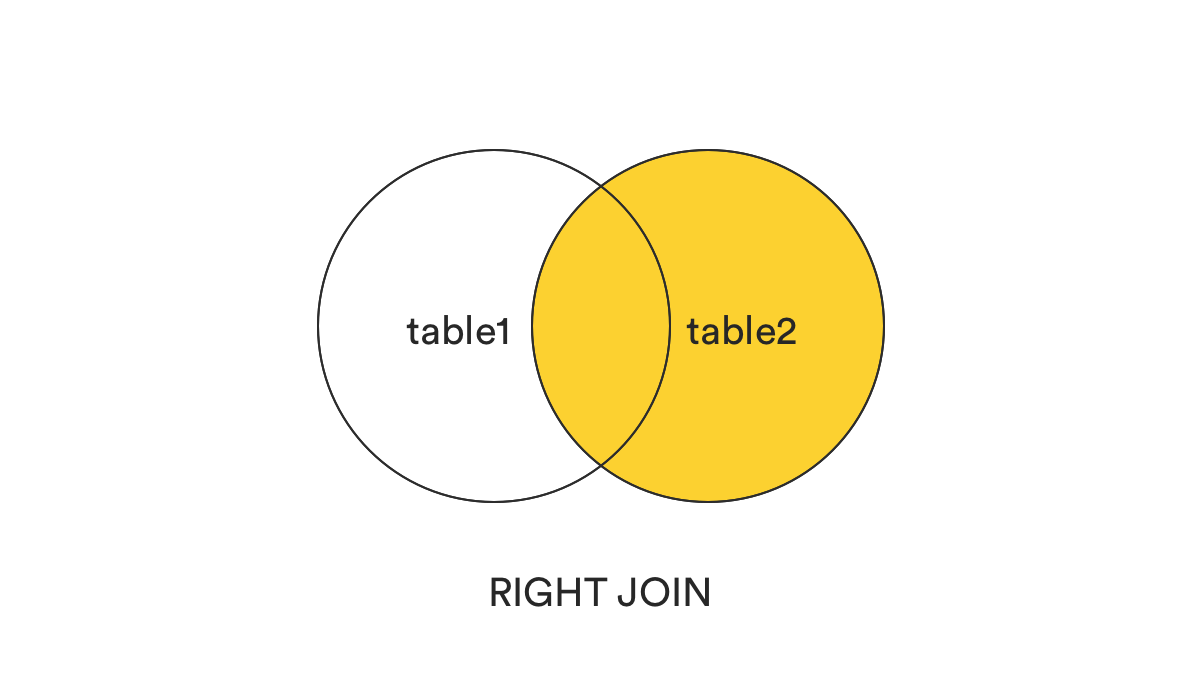
6. RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN
In the opposite of LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN returns all records from the right table (table2) that matched the ON condition.
SQL syntax:
SELECT *
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2;
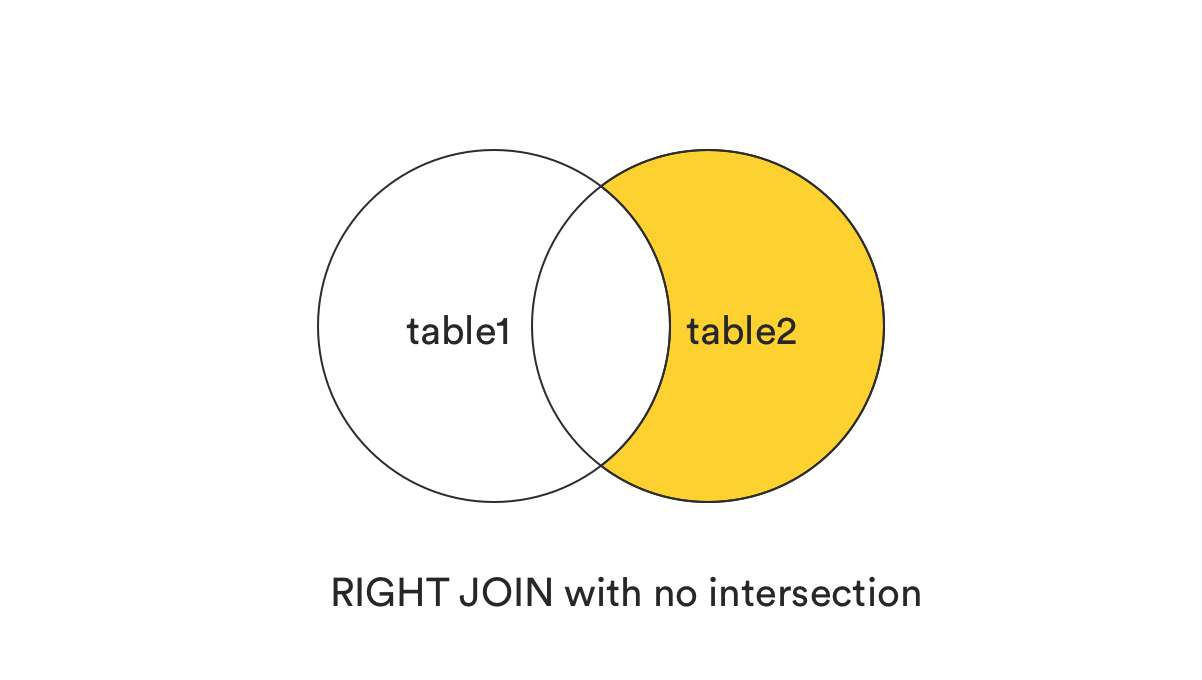
7. RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN without the intersection
This clause returns all records from the right table (table2) that matched the ON condition, but exclude those are in common better two tables, or those records exist in both tables.
In plain term, it can be understood as (RIGHT JOIN) - (INNER JOIN).
SQL syntax:
SELECT *
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2
ON table1.col1 = table2.col2
WHERE table1.col1 IS NULL;
Need a good GUI tool to work with SQL databases? TablePlus provides a modern, native tool with intuitive UI to manage multiple relational databases in cluding SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Oracle…
And it’s available for free!
Not on Mac? Download TablePlus for Windows.
On Linux? Download TablePlus for Linux
Need a quick edit on the go? Download TablePlus for iOS.